Complete Guide to CURP, RFC, and CLABE in México [2025]
September 3, 2025
8 minutes read
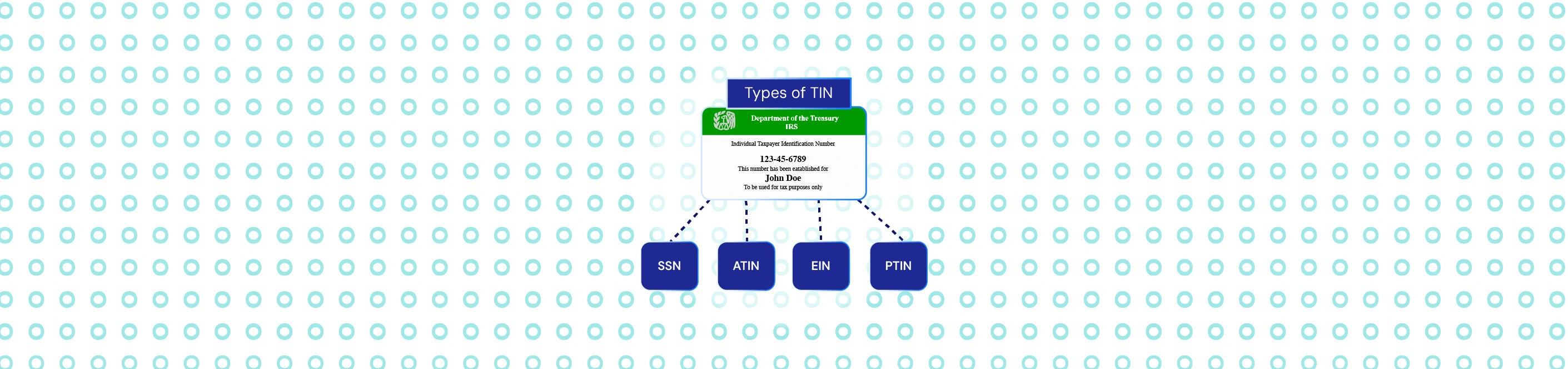
- Clave Única de Registro de Población (CURP) handles individual identification within the government system.
- CFDI v4.0 requires exact RFC name and address matching against SAT’s database, making customer RFC validation critical for invoicing.
- CLABE payments through SPEI are irreversible once processed, making upfront verification essential before sending any electronic transfers.
I was grabbing lunch with a consultant friend who had just finished helping a tech company set up their México operations.
‘You know what’s funny?’ she said, ‘Everyone panics about the Mexican bureaucracy, but their identification system is actually pretty logical once you see the big picture.’
She explained how this company had been dreading the compliance setup, expecting months of back-and-forth with government offices. Instead, they got everything sorted in a few weeks.
Curious, I asked what made the difference.
She mentioned that México uses specific identification codes that work together, and most companies struggle because they don’t understand this system upfront.
My curious brain couldn’t let it go, so I started asking around and doing some research. It turns out there’s a clear pattern – companies that nail their México setup versus those that struggle all come down to three codes: CURP, RFC, and CLABE.
Here’s everything you need to know about how these work.
How CURP, RFC, and CLABE Work in México
Unlike many countries that try to use one number for everything, México designed three separate codes that work together without overlap.
- Clave Única de Registro de Población (CURP) handles individual identification within the government system.
- Registro Federal de Contribuyentes (RFC) manages all tax-related activities and business registration.
- Clave Bancaria Estandarizada (CLABE) processes banking transactions and electronic payments.
Each code has its own lane and stays in it, which actually makes the system more predictable once you understand the logic.
| 💡The preferred approach is obtaining these codes in sequence: start with CURP since it’s required for RFC applications, then get your RFC for business operations, and finally set up your CLABE through banking once your business registration is complete. |
The smart part is how they complement each other in business operations. Here’s a quick reference table covering the essentials of all three codes.
| Aspect | CURP | RFC | CLABE |
| Issued By | RENAPO (National Population Registry) | SAT (Tax Administration Service) | ABM/Banco de México (Banking Association/Central Bank) |
| Format | 18 alphanumeric characters | 12-13 alphanumeric characters | 18 numeric digits |
| Primary Business Use | Employee registration, legal representatives | Invoicing, contracts, tax filings | Wire transfers, vendor payments, payroll deposits |
| Required For | Payroll setup, HR systems | Business operations, bank accounts | Electronic fund transfers, SPEI payments |
| Verification/validation | RENAPO portal, SIgnzy CURP Verification API | SAT portal (up to 5,000 records), Signzy RFC Fetch API | Bank systems, CLABE validators |
Now, let’s discuss the specifics of each.
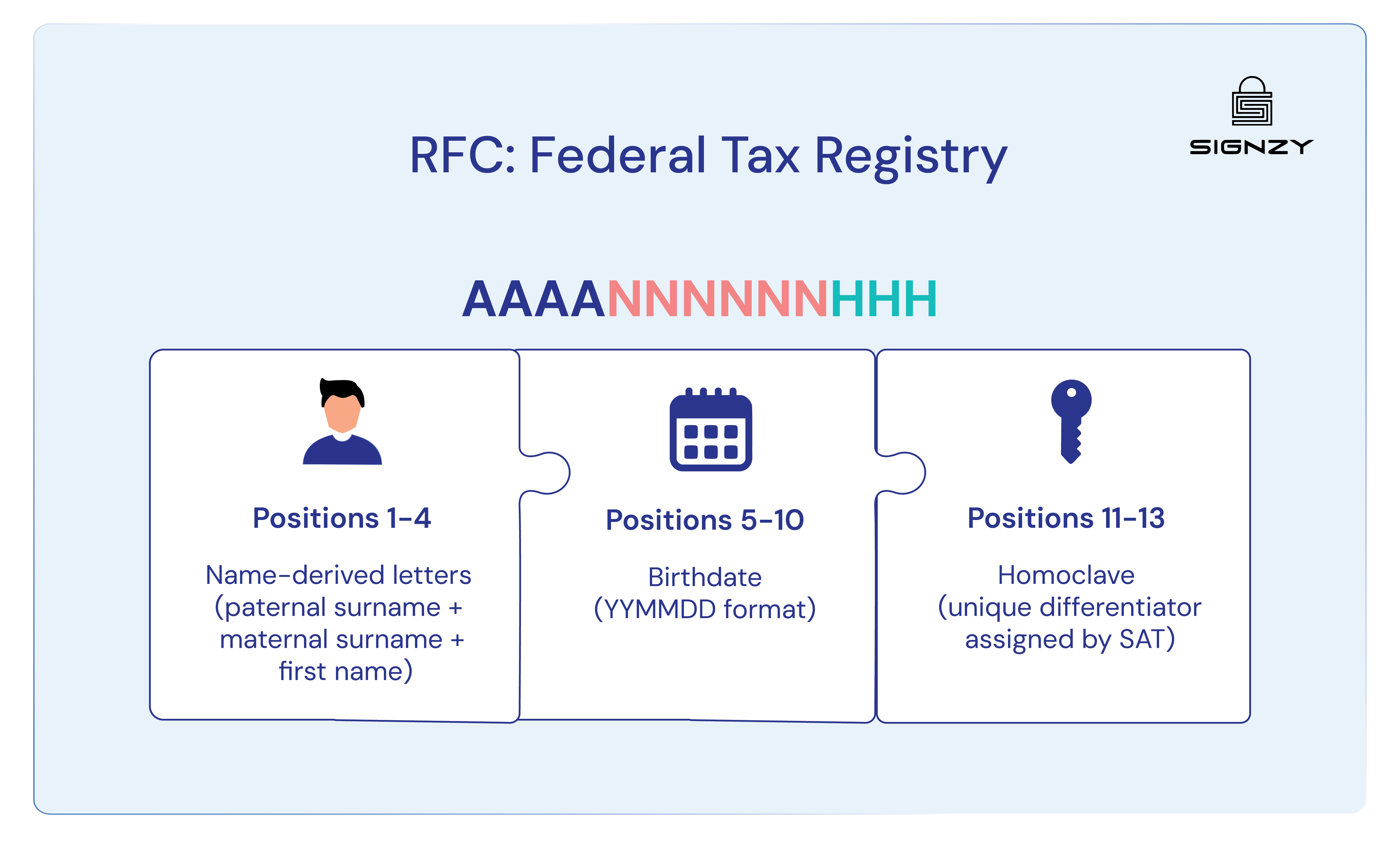
Getting RFC Requirements Right in México
RFC management across your business ecosystem affects everything from payroll processing to tax audit outcomes. Understanding the nuances of each relationship type prevents compliance gaps that can cost significant time and money to resolve.
Your Team’s RFCs
Employee RFC requirements vary by immigration status. Mexican nationals apply immediately with their CURP, while foreign employees can apply with temporary residency, permanent residency, or even tourist visas (FMM) accompanied by valid passports.
The timing matters – RFC applications through citas.sat.gob.mx takes 4-6 weeks from scheduling to completion. Employees without RFCs can’t be properly added to IMSS or have accurate tax withholdings calculated.
Online applications work for basic payroll needs, but employees planning to buy property or frequently update information should complete in-person applications for e-Firma digital signature access.
Customer RFCs for Invoicing
CFDI v4.0 validation requires RFC names and postal codes matching SAT’s Constancia de Situación Fiscal database. Mismatches result in invoice rejection and payment delays.
For businesses, ensure customers provide exact legal entity names excluding suffixes like “S.A. de C.V.” For individuals without RFCs, use generic codes: XAXX010101000 for Mexican residents, XEXX010101000 for foreigners.
High-volume operations should implement real-time RFC validation APIs to prevent rejected CFDIs and payment delays.
Vendor RFCs for Expenses
Vendor RFC validation directly impacts deductible expense calculations. SAT disallows expenses paid to inactive, suspended, or blacklisted vendors entirely.
Verify vendor business activities match their RFC registration – mismatches flag during audits and invalidate expense categories. Implement quarterly vendor RFC status checks rather than annual reviews to catch problems early.
Getting CURP Requirements Right in México
CURP verification isn’t optional for most businesses, but the rules around when and how to do it aren’t well explained anywhere. Here’s what actually matters for compliance.
Employee CURP Verification
Collecting CURP numbers from employees is the easy part. The real challenge starts when you realize you need to actually verify these things through RENAPO’s system. Can’t just trust what people hand you – fake CURP documents are everywhere, and using them creates a mess with IMSS and tax filings later.
Foreign employees on tourist visas literally cannot get legitimate CURP. Zero chance. Only residents and citizens qualify. Yet staffing agencies keep sending tourist visa workers with sketchy documentation, and companies don’t realize they’re violating regulations until an audit hits.
This verification has to happen before you touch IMSS or submit payroll taxes. Invalid CURP in those systems is like waving a red flag at regulators – suddenly, they’re looking at everything you do much more closely.
Customer CURP Requirements
Customer CURP verification is part of Know Your Customer compliance in México. It goes way beyond checking if the format looks right. You’re supposed to confirm this person actually exists, isn’t dead, and that their personal details match what they told you.
Sounds basic, but the government databases will surprise you with how often people are using dead relatives’ information. There are some prevention steps as well:
- Run database validation during account opening to catch fraudulent documentation before it enters your systems
- Cross-reference high-value customers against multiple verification sources and flag inconsistencies for manual review
- Monitor for identity fraud patterns like mismatched personal details or customers using relatives’ documentation
- Implement real-time CURP verification during transaction processing to prevent payments to invalid accounts
The automated systems catch obvious fraud, but sophisticated schemes need human reviewers to spot the patterns that machines miss.
Ongoing CURP Monitoring
CURP information changes when people die, move, or update their immigration status. Your systems should be watching for these changes automatically instead of waiting for your annual compliance review to catch problems.
When processing transactions, you want CURP validation to happen in real-time. This prevents payments from going to dead people or fake accounts. Much easier to stop fraud before it happens than to explain it to regulators after the fact.
Getting CLABE Requirements Right in México
CLABE numbers control every electronic payment in México. Mess this up, and your transfers fail, creating customer service and compliance problems.
CLABE Collection and Verification
Every vendor payment, customer refund, and payroll deposit needs a valid CLABE. The 18-digit format includes bank code, branch location, account number, and control digit – when any part is wrong, payments bounce immediately.
Most businesses just collect CLABE numbers without verification. Bad move. You need to validate the control digit and confirm the bank code exists before processing anything.
| CLABE Component | Digits | Purpose |
| Bank Code | 3 | Identifies financial institution |
| Branch Code | 3 | Specific bank location |
| Account Number | 11 | Individual account identifier |
| Control Digit | 1 | Validates entire CLABE |
Also, it’s important to note that CLABE numbers change when customers switch banks or account types, so outdated information creates payment failures.
Payment Processing Reality
SPEI payments are irreversible once sent. Unlike wire transfers, you can’t recall them if something goes wrong. This makes upfront CLABE verification important rather than optional.
Too many failed payments flags your company during regulatory reviews. Implement real-time validation during payment setup rather than discovering problems after failed transfers. Some customers provide CLABE numbers belonging to other people, creating compliance issues for regulated businesses that must verify account ownership.
That’s it For Today on CURP, RFC, and CLABE.
Thanks for reading through all the México compliance details with me! I know it’s a lot to digest, but getting these three codes right makes everything else so much smoother.
We have separate guides on RFC and CURP as well, so check out our related blogs below if you want to dive deeper into either topic.
And if you’re looking to automate RFC or CURP verification instead of handling it manually, Signzy can help automate that process as well (while staying compliant, of course!). If you want to see exactly how, book your demo here.
FAQs
What happens if we process payroll with invalid employee CURP numbers?
IMSS will reject enrollment, tax filings get flagged, and labor inspectors may issue violations during audits. Always verify CURP authenticity before payroll setup.
Can we use the same RFC for multiple business entities in México?
No. Each legal entity needs its own RFC registration. Using one RFC across multiple entities violates tax regulations and creates compliance issues.
How do we handle CLABE verification for high-volume vendor payments?
Implement automated CLABE validation APIs that check format and bank codes in real time during payment setup rather than manual verification.
Do we need customer RFC for all invoices or just certain transaction types?
CFDI v4.0 requires RFC for all business invoices. Use generic RFCs when customers don’t provide specific numbers to maintain compliance.